When conducting research for website effectiveness, it is crucial to consider both direct and indirect competition.
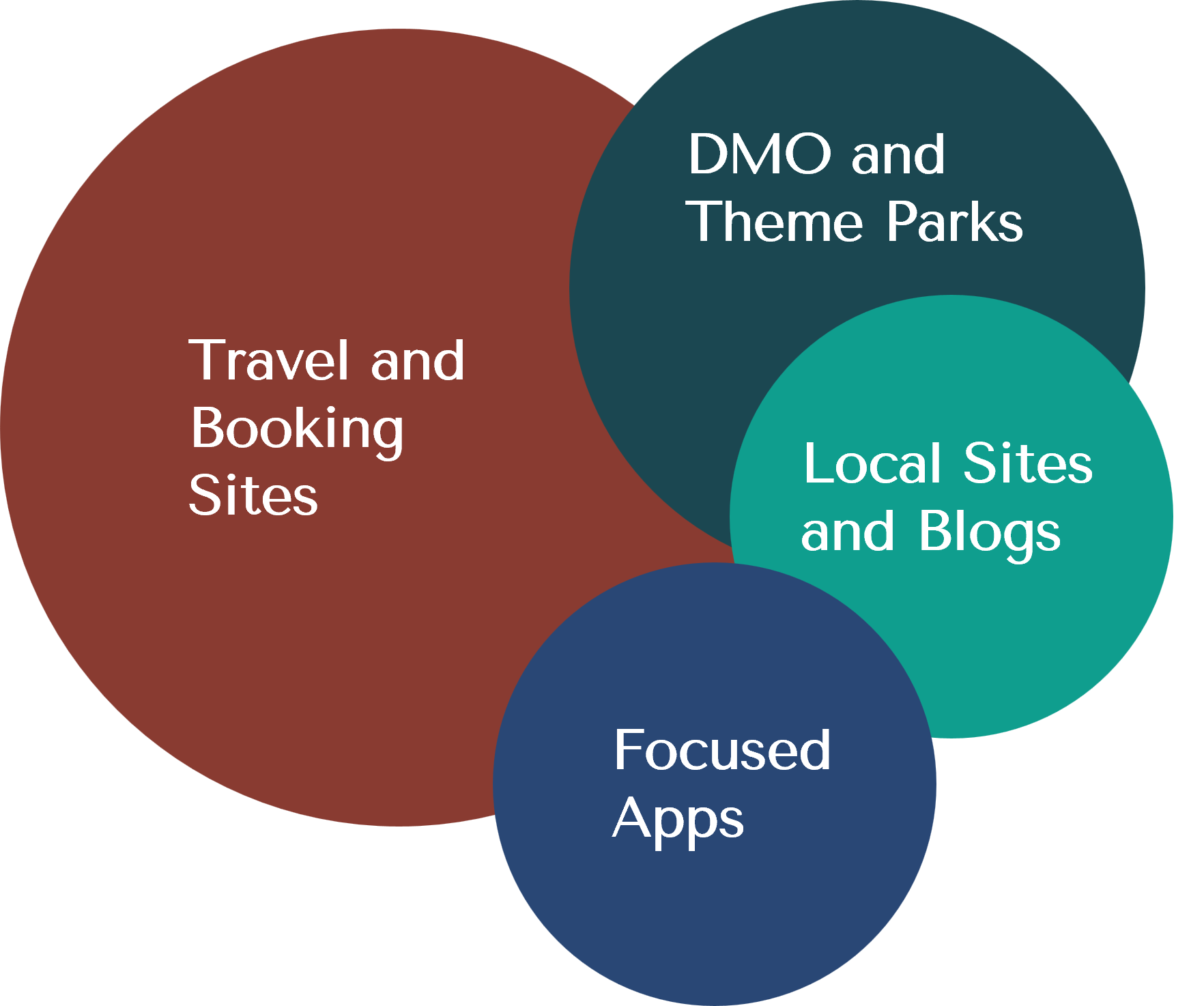
Here is an example of competition faced by a destination visitor website such as nycgo.com, visitlasvegas.com, or visitorlando.com.
Each sub-category of sites has its own rules of competition that must be clearly understood. For example, travel and booking sites optimize their content to encourage users to visit their site and complete a booking.
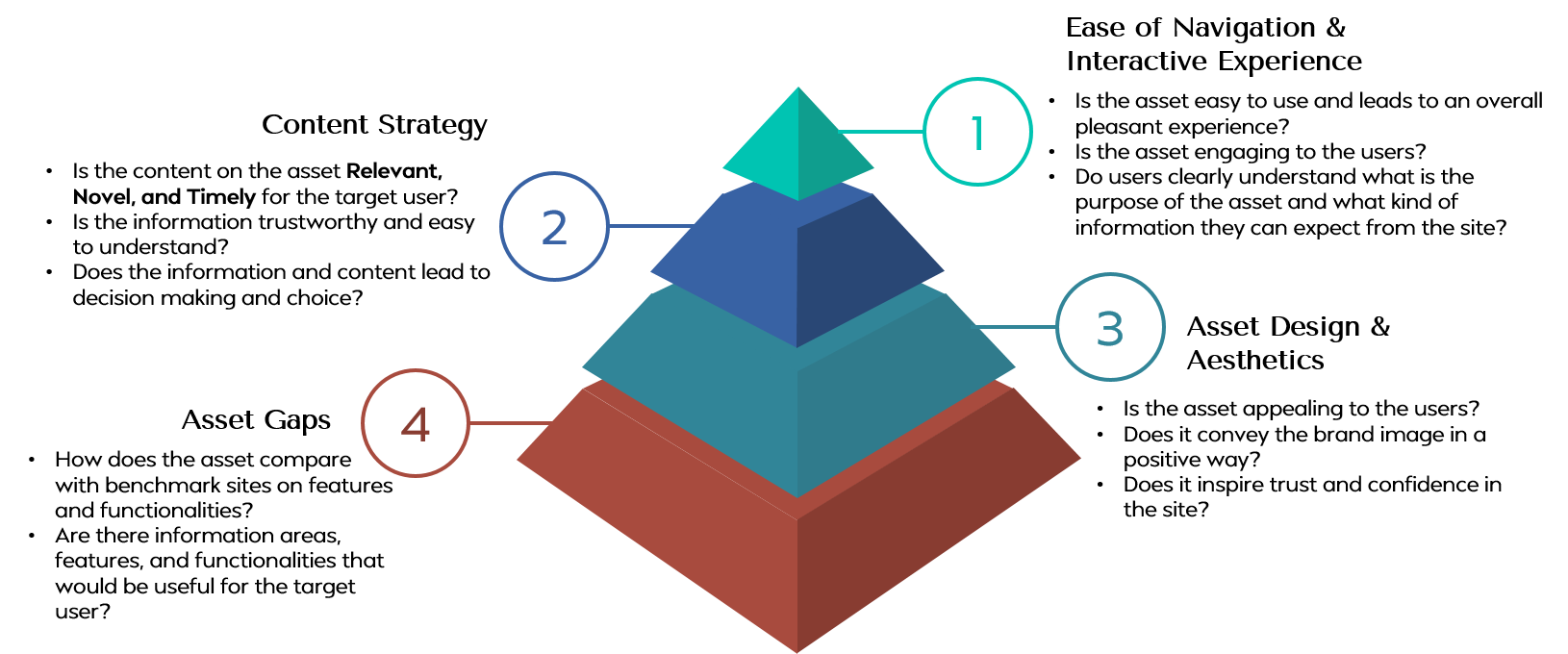
The Home Page design is positioned as the first step to complete Travel Logistics.
Most Effective Sites provide a Shortcut to Narrow Choices.
All Relevant Information for Decision-Making Is in One Place.
Show User-Generated Content to engage the Audience and stimulate vicarious travel experience.
The Best Sites provide great Browsing Experience.
Sites offer useful, Well-Designed Tools that make decision-making tasks easy.
Such rules of competition would differ among various sub-categories. A competitive analysis must consider each sub-category and how they overlap with each other. Most innovative and compelling strategies emerge from such analysis of cross-category competition. Taking the best-in-class ideas from various sub-categories also provides an immense source of valuable ideas to copy and imitate on the client site.
| Site Objectives | What are the primary goals of the site? |
| Competitive Strategy | What is the competitive formula? |
| Site Positioning | What are the primary dimensions? |
| Target Segment | Which target segments does it serve? |
| Home Page | Task framing on the home / hub pages |
| Menu | Structure, Labels |
| Navigation | Active vs. Passive |
| Functionalities | Search, Interactive or Decision Tools |
| Format | Mobile vs. Desktop |
| Information Value | Novelty, Relevance, Comprehension, Trust |
| Interactive Experience | Accurate Results, Pleasant, Flow |
| Image | Aesthetics, Tone |
| Decision Making | Decision Aids, Able to Close |
| Relationship | Intention to Revisit, For Me |
| Site Equity | Opinion, Attitude, Value |
Redesigning a website offers new opportunities to redefine the competition, reposition the website to new and diverse audiences, and create compelling pathways for conversion. However, multiple steps are involved in conducting research for a strategic redesign project.
WHAT DRIVES USER CHOICE?
Consumers are invited to the lab in a simulated environment to visit the client and competitive best in class sites to understand decision making. A psychometric model is used to quantitatively assess drivers of choice and identify best in class site elements and content.

BUILD AND TEST FROM THE BEST
The findings from the first phase is used to assemble examples that are best in class or most effective from competitive sites to use in exploration with consumers in next phase.
Note: Research prototype is only meant for research purposes and does not have design, aesthetic, and functional properties of a real website.

BUILD AND TEST FROM THE BEST
Research prototype and concepts are used to conduct a deep dive with consumers. The exploration is done in mini focus group sessions. The sessions are used to verify and further develop the ideas that emerged from the diagnostic phase. The final recommendations are based on this phase.
1. A lab study is conducted to identify competitive drivers of choice and the best-in-class elements.


Respondents complete a three-part lab:

Report with website ratings and market drivers per region, hospital, disease state, and consumer segment
2. Collaborative ideation sessions are conducted between the client, agency, and research team.

Collaborative meetings between the Client, agency, and C3R to discuss ways to elevate Brand, Content, and Experience based on Phase I results.
3. Research Prototype development and testing

C3R Weblab or the Agency develops realistic, detailed, and clickable prototypes for exposure to participants in Phase III Ideation Sessions.

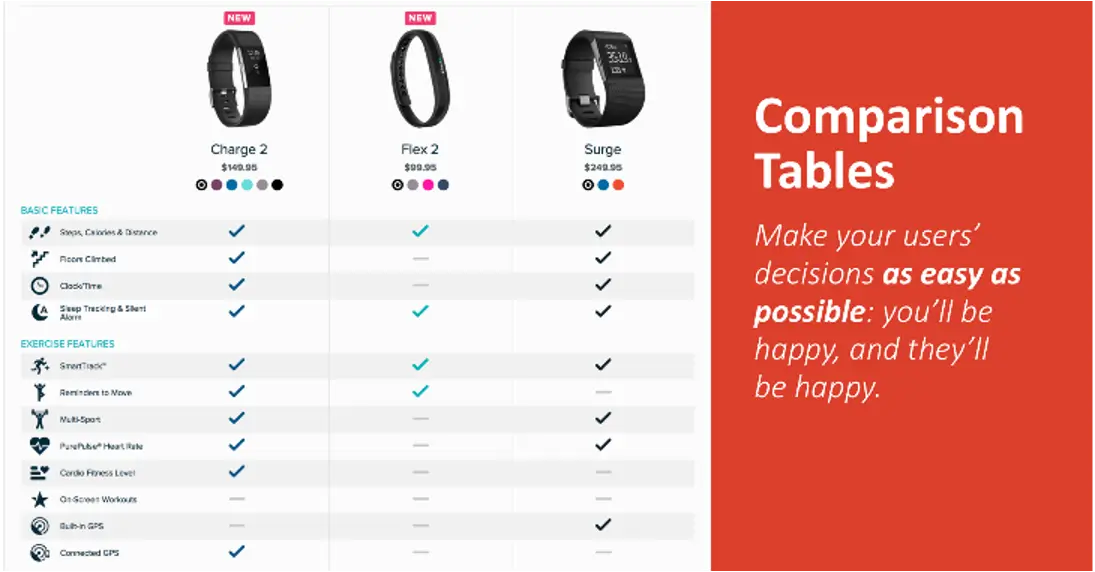
I3R Web Brand Equity ModelTM is used to improve digital assets such as Interactive Point of Sale, Product comparison tools, and Microsites.
Hospital Sites are at the End of the Decision-Making Chain.
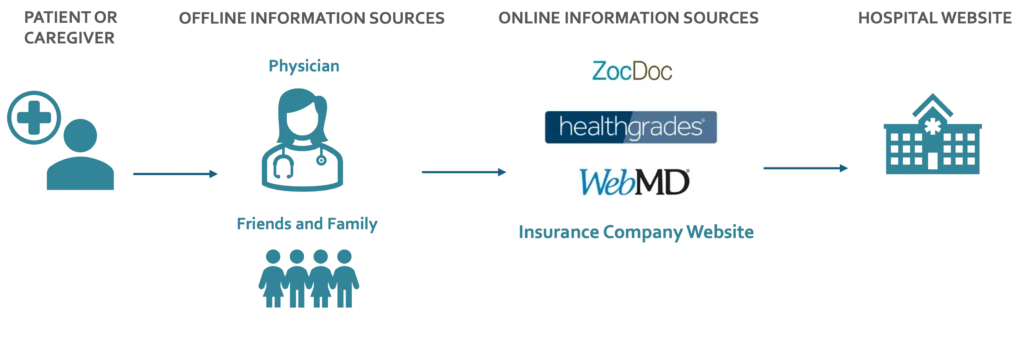
Strategic redesign results in a consumer-centric healthcare website that enables consumers to navigate the site confidently and make informed healthcare decisions.

We’d love to hear from you!
Please enter your contact details if you want to know how we can help your business through strategic research, UX/UI design, or brand innovation.
